Legal basis (in Polish law)
Rozdział 2
Stanowisko kontrolne
…
§ 14.2. Stanowisko okręgowej stacji kontroli pojazdów oraz stacji , o której mowa w art.83 ust.1 pkt.1 lit. b ustawy z dnia 20 czerwca 1997 r.- prawo o ruchu drogowym, powinno być wyposażone w:
…
2) elektroniczny detektor gazów do kontroli nieszczelności instalacji gazowej,
…
§ 15. Wyposażenie technologiczne stanowiska kontrolnego powinno obejmować co najmniej:
…
4) wentylację naturalną oraz mechaniczną nawiewno-wywiewną, zapewniającą dodatkową awaryjną wymianę powietrza, przy czym stanowisko kontrolne powinno być wyposażone w alarmowy czujnik niedopuszczalnego poziomu tlenku węgla, który automatycznie uruchamia tryb awaryjny wentylacji,
…
7) alarmowy czujnik nadmiernego poziomu gazu płynnego i ziemnego w stacji kontroli pojazdów przeprowadzającej badania pojazdów przystosowanych do zasilania gazem.
§ 1. 1. Ustala się wartości najwyższych dopuszczalnych stężeń chemicznych i pyłowych czynników szkodliwych dla zdrowia w środowisku pracy, określone w wykazie stanowiącym załącznik nr 1 do rozporządzenia.
2. Ustala się wartości najwyższych dopuszczalnych natężeń fizycznych czynników szkodliwych dla zdrowia w środowisku pracy, określone w wykazie stanowiącym załącznik nr 2 do rozporządzenia.
§ 2. Wartości, o których mowa w § 1 ust. 1, określają najwyższe dopuszczalne stężenia czynników szkodliwych dla zdrowia, ustalone jako:
1) najwyższe dopuszczalne stężenie (NDS) — wartość średnia ważona stężenia, którego oddziaływanie na pracownika w ciągu 8-godzinnego dobowego i przeciętnego tygodniowego wymiaru czasu pracy, określonego w ustawie z dnia 26 czerwca 1974 r. – Kodeks pracy, przez okres jego aktywności zawodowej nie powinno spowodować ujemnych zmian w jego stanie zdrowia oraz w stanie zdrowia jego przyszłych pokoleń;
2) najwyższe dopuszczalne stężenie chwilowe (NDSCh) — wartość średnia stężenia, które nie powinno spowodować ujemnych zmian w stanie zdrowia pracownika, jeżeli występuje w środowisku pracy nie dłużej niż 15 minut i nie częściej niż 2 razy w czasie zmiany roboczej, w odstępie czasu nie krótszym niż 1 godzina;
3) najwyższe dopuszczalne stężenie pułapowe (NDSP) — wartość stężenia, która ze względu na zagrożenie zdrowia lub życia pracownika nie może być w środowisku pracy przekroczona w żadnym momencie.
Dział III
Budynki i pomieszczenia
Rozdział 10
Garaże dla samochodów osobowych
…
§ 108.1. W garażu zamkniętym należy stosować wentylację:
…
3) mechaniczną, sterowaną czujkami niedopuszczalnego poziomu stężenia tlenku węgla - w innych garażach, niewymienionych w pkt 1 i 2, oraz w kanałach rewizyjnych, służących zawodowej obsłudze i naprawie samochodów bądź znajdujących się w garażach wielostanowiskowych, z zastrzeżeniem § 150 ust. 5.
4) mechaniczną, sterowaną czujkami niedopuszczalnego poziomu stężenia gazu propan-butan - w garażach, w których dopuszcza się parkowanie samochodów zasilanych gazem propan-butan i w których poziom podłogi znajduje się poniżej poziomu terenu.
…
Detected substance/property
- Substance/property:
- carbon monoxide (CO) §
- Hazard:
- toxic gas
- LEL (lower explosive limit):
- 12.5 %v/v
- TWA (time-weighted average):
- 23.0 mg/m3
- STEL (short-term exposure limit):
- 117.0 mg/m3
- Density relative to air:
- 0.97
- Substance/property:
- liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) §
- Hazard:
- explosive gas
- LEL (lower explosive limit):
- 2.1 %v/v
- Density relative to air:
- 1.8
- Substance/property:
- hydrogen (H2)
- Hazard:
- explosive gas
- LEL (lower explosive limit):
- 4.0 %v/v
- Density relative to air:
- 0.07
- Substance/property:
- nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
- Hazard:
- toxic gas
- TWA (time-weighted average):
- 0.2 mg/m3
- STEL (short-term exposure limit):
- 0.5 mg/m3
- Density relative to air:
- 1.58
Location of detectors
- Carbon monoxide (CO): on support structure poles or walls; 1.6-1.8 m above floor level; detection area ≈ circle with radius 8 m;
- Propane-butane (LPG): on support structure columns or walls; lower edge of detector approx. 30 cm above floor level; away from exhaust openings in case of ducted ventilation.
- Propane-butane (LPG) in diagnostic ducts: lower edge of detector approx. 30 cm above floor level; away from exhaust openings.
- Standard solution – installation in pairs, LPG detector supplied from CO detector.
- Hydrogen: bottom edge of detector approx. 30 cm below ceiling level; away from supply air vents, window and door openings.
- Nitrogen oxides: on supporting structure columns or walls; 1.6-1.8 m above floor level.
- In a place not subject to the direct influence of water vapour, liquids, flue gases.
- Away from supply air vents, window and door openings.
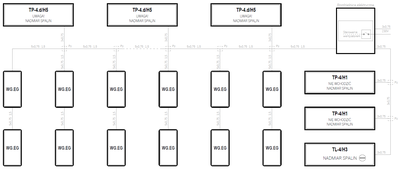
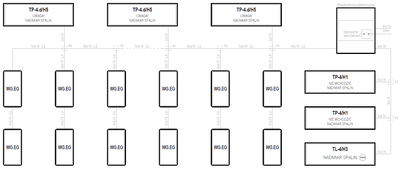
Standard configurations of gas detection systems
- System topology
- Serial (linear)
- Supply voltage
- 230VAC
- Maximum number of gas detectors
- ∞
- Emergency power backup
- —

Sensor semiconductor

Sensor semiconductor

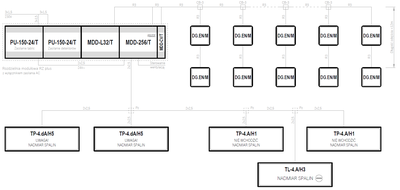
- System topology
- Bus
- Supply voltage of the control unit
- 24VDC
- Control unit
- MDD-256/T
- Maximum number of gas detectors
- 224
- Emergency power backup
- —

Sensor semiconductor

Sensor semiconductor









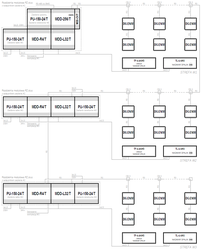
- System topology
- Bus
- Supply voltage of the control unit
- 24VDC
- Control unit
- MDD-256/T
- Maximum number of gas detectors
- 224
- Emergency power backup
- —

Sensor semiconductor

Sensor semiconductor










Legal basis (in Polish law)
Rozdział 2
Stanowisko kontrolne
…
§ 14.2. Stanowisko okręgowej stacji kontroli pojazdów oraz stacji , o której mowa w art.83 ust.1 pkt.1 lit. b ustawy z dnia 20 czerwca 1997 r.- prawo o ruchu drogowym, powinno być wyposażone w:
…
2) elektroniczny detektor gazów do kontroli nieszczelności instalacji gazowej,
…
§ 15. Wyposażenie technologiczne stanowiska kontrolnego powinno obejmować co najmniej:
…
4) wentylację naturalną oraz mechaniczną nawiewno-wywiewną, zapewniającą dodatkową awaryjną wymianę powietrza, przy czym stanowisko kontrolne powinno być wyposażone w alarmowy czujnik niedopuszczalnego poziomu tlenku węgla, który automatycznie uruchamia tryb awaryjny wentylacji,
…
7) alarmowy czujnik nadmiernego poziomu gazu płynnego i ziemnego w stacji kontroli pojazdów przeprowadzającej badania pojazdów przystosowanych do zasilania gazem.
§ 1. 1. Ustala się wartości najwyższych dopuszczalnych stężeń chemicznych i pyłowych czynników szkodliwych dla zdrowia w środowisku pracy, określone w wykazie stanowiącym załącznik nr 1 do rozporządzenia.
2. Ustala się wartości najwyższych dopuszczalnych natężeń fizycznych czynników szkodliwych dla zdrowia w środowisku pracy, określone w wykazie stanowiącym załącznik nr 2 do rozporządzenia.
§ 2. Wartości, o których mowa w § 1 ust. 1, określają najwyższe dopuszczalne stężenia czynników szkodliwych dla zdrowia, ustalone jako:
1) najwyższe dopuszczalne stężenie (NDS) — wartość średnia ważona stężenia, którego oddziaływanie na pracownika w ciągu 8-godzinnego dobowego i przeciętnego tygodniowego wymiaru czasu pracy, określonego w ustawie z dnia 26 czerwca 1974 r. – Kodeks pracy, przez okres jego aktywności zawodowej nie powinno spowodować ujemnych zmian w jego stanie zdrowia oraz w stanie zdrowia jego przyszłych pokoleń;
2) najwyższe dopuszczalne stężenie chwilowe (NDSCh) — wartość średnia stężenia, które nie powinno spowodować ujemnych zmian w stanie zdrowia pracownika, jeżeli występuje w środowisku pracy nie dłużej niż 15 minut i nie częściej niż 2 razy w czasie zmiany roboczej, w odstępie czasu nie krótszym niż 1 godzina;
3) najwyższe dopuszczalne stężenie pułapowe (NDSP) — wartość stężenia, która ze względu na zagrożenie zdrowia lub życia pracownika nie może być w środowisku pracy przekroczona w żadnym momencie.
Dział III
Budynki i pomieszczenia
Rozdział 10
Garaże dla samochodów osobowych
…
§ 108.1. W garażu zamkniętym należy stosować wentylację:
…
3) mechaniczną, sterowaną czujkami niedopuszczalnego poziomu stężenia tlenku węgla - w innych garażach, niewymienionych w pkt 1 i 2, oraz w kanałach rewizyjnych, służących zawodowej obsłudze i naprawie samochodów bądź znajdujących się w garażach wielostanowiskowych, z zastrzeżeniem § 150 ust. 5.
4) mechaniczną, sterowaną czujkami niedopuszczalnego poziomu stężenia gazu propan-butan - w garażach, w których dopuszcza się parkowanie samochodów zasilanych gazem propan-butan i w których poziom podłogi znajduje się poniżej poziomu terenu.
…
Detected substance/property
- Substance/property:
- carbon monoxide (CO) §
- Hazard:
- toxic gas
- LEL (lower explosive limit):
- 12.5 %v/v
- TWA (time-weighted average):
- 23.0 mg/m3
- STEL (short-term exposure limit):
- 117.0 mg/m3
- Density relative to air:
- 0.97
- Substance/property:
- liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) §
- Hazard:
- explosive gas
- LEL (lower explosive limit):
- 2.1 %v/v
- Density relative to air:
- 1.8
- Substance/property:
- carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Hazard:
- toxic gas
- TWA (time-weighted average):
- 9000.0 mg/m3
- STEL (short-term exposure limit):
- 27000.0 mg/m3
- Density relative to air:
- 1.52
- Substance/property:
- hydrogen (H2)
- Hazard:
- explosive gas
- LEL (lower explosive limit):
- 4.0 %v/v
- Density relative to air:
- 0.07
- Substance/property:
- methane (CH4)
- Hazard:
- explosive gas
- LEL (lower explosive limit):
- 4.4 %v/v
- Density relative to air:
- 0.55
- Substance/property:
- nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
- Hazard:
- toxic gas
- TWA (time-weighted average):
- 0.2 mg/m3
- STEL (short-term exposure limit):
- 0.5 mg/m3
- Density relative to air:
- 1.58
Location of detectors
- Carbon monoxide (CO): on support structure columns or walls; 1.6-1.8 m above floor level; detection area ≈ circle with radius 8 m.
- Propane-butane (LPG): on support structure columns or walls; lower edge of detector approx. 30 cm above floor level; away from exhaust openings in case of ducted ventilation.
- Standard solution – installation in pairs, LPG detector supplied from CO detector.
- Propane-butane (LPG) in diagnostic ducts: lower edge of detector approx. 30 cm above floor level; away from exhaust openings.
- Methane (CNG, LNG): lower edge of detector approx. 30 cm below floor level; away from supply air vents, window and door openings.
- Nitrogen oxides: on supporting structure columns or walls; 1.6-1.8 m above floor level.
- Carbon dioxide: on supporting structure columns or walls; 1.6-1.8 m above floor level.
- Hydrogen: bottom edge of detector approx. 30 cm below ceiling level; away from supply air vents, window and door openings.
- In a location not subject to the direct influence of water vapour, liquids, flue gases.
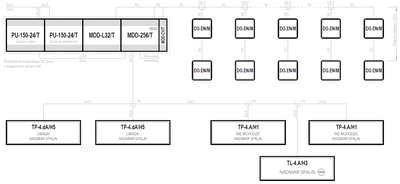
Standard configurations of gas detection systems
- System topology
- Serial (linear)
- Supply voltage
- 230VAC
- Maximum number of gas detectors
- ∞
- Emergency power backup
- —

Sensor semiconductor

Sensor semiconductor

- System topology
- Bus
- Supply voltage of the control unit
- 24VDC
- Control unit
- MDD-256/T
- Maximum number of gas detectors
- 224
- Emergency power backup
- —

Sensor semiconductor

Sensor semiconductor